BIDV_EN Library / Common_EN / HTML Tab / Coporate / Tab Menu Guid Legal Procedures
BIDV_EN Library / Corporate / Corporate Client / Legal Procedure
Investment procedures, law, regulations and Frequently Asked Questions for Foreign investors investing in Vietnam.
Investment procedures, law, regulations and Frequently Asked Questions for Foreign investors investing in Vietnam.
BIDV_EN Library / Common_EN / Coporate / Tab Menu / Common / Tab Menu_Legal Procedure
FAQS
a, Assurance of Business Investment
Vietnamese Government recognizes and protects asset ownership, freedom of business of foreign investors in Vietnam. Some main points as below:
- Lawful assets of investors shall not be nationalized or confiscated by administrative measures.
- After all financial obligations to Vietnamese Government are fulfilled, foreign investors are permitted to transfer the Capital, income and other assets overseas.
- Investors are not required to buy or use domestic goods/services or reach a certain rate of import substitution; No restriction in value and export/import ratio.
- Where a new law is promulgated, investors can choose whether to keep the old investment incentives or enjoy new incentives, whichever more favorable. In the case that an investor is no longer eligible for investment incentives because legal regulations are changed for reasons of national defense and security, social order and security, social ethics, public health, or environmental protection, they shall receive compensation from the Government
b, Investment incentives
Vietnamese Government gives investment incentives and support for investment projects: (1) relating to high-tech activities, information technology, agriculture, education, healthcare, renewable energy, etc.; (2) in disadvantaged area or extremely disadvantaged areas; in industrial parks, export-processing zones, hi-tech zones, economic zones; in a rural area that employ at least 500 workers; (3) having capital investment of at least 6,000 billion dong.
c, Forms of incentives
- Exemption, reduction or lower rate of corporate income tax.
- Exemption of import duties on goods, machinery, equipment used for the project.
- Exemption or reduction of land lease, property tax, land using fees.
Pursuant to:
Article 9 – Article 11, Article 14, Article 15, Article 16, Law on Investment 2014.
a, Establishment of new legal entity in Vietnam
This is the most common way that foreign investors use when investing in Vietnam.
- Advantages: Transparency. Foreign investors can participate in the ownership and management of the company right at the beginning.
- Disadvantages: Complex investment procedure. It takes much longer time than the methods of Capital contribution, Purchase of shares/capital contribution portion in existing Vietnamese company.
b, Capital contribution, Purchase of shares/capital contribution portion in enterprises operating in Vietnam (existing Vietnamese company).
- Advantages: Simple investment procedure, much faster than “establishment of new legal entity”; be able to utilize licenses, land, property, workforce, market share, etc. of existing Vietnamese company.
- Disadvantages: Require time and effort to do research, evaluation, appraisal of Target Company.
c, Investment under Public-Private Partnership Contract (PPP): Investors and project management companies shall sign PPP contracts with competent authorities to execute an investment project to build new infrastructure works, to improve, upgrade, expand, manage, and operate infrastructure works, or to provide public services.
d, Investment under Business Cooperation Contract (BCC): Investors sign BCC contract to do business collaboration. Products and P&L are shared among investors without establishment of new legal entity.
Pursuant to:
Article 22-Article 29, Law on Investment 2014.
a, Single member limited liability company (LLC): Enterprises whose ownership consists of only one (1) organization/individual. The owner has full authority in making decisions regarding the operation of the company; and is liable for debts and other liabilities up to the value of charter capital.
b, Multi-member LLC: Members are liable for debts and other liabilities up to the value of capital they have contributed to the business. Members can be either organization or individual, minimum of two (02) and maximum of (fifty) 50 members.
c, Joint-stock Company (JSC)
Companies that have the following features:
- Charter capital is split into multiple units of equal value called shares;
- Minimum of three (3) shareholders, maximum is not restricted. Shareholders are liable for debts and other liabilities up to the value of capital they have contributed to the company. Shareholders are entitled to transfer their shares to others; except for Founding Shareholders are restricted within the first 3 years from the issuance date of the Certificate of Business registration: (1) only able to transfer their shares to other founding shareholders, (2) able to transfer to others only if it is approved by the General Meeting of Shareholders.
- JSC can issue more shares to increase charter capital.
d, Partnership
Companies that have the following features:
- At least two (02) partners are co-owners of the company who run business together in a common name (hereinafter referred to as unlimited liability partners.
- Unlimited liability partners are individuals who are responsible for the company’s obligations with all of their property.
- Beside unlimited liability partners, a partnership may have limited liability partners. Limited liability partners are only liable for the company’s debts and other liabilities up to the value of capital they contributed to the company.
Pursuant to:
- Law on Enterprises 2014
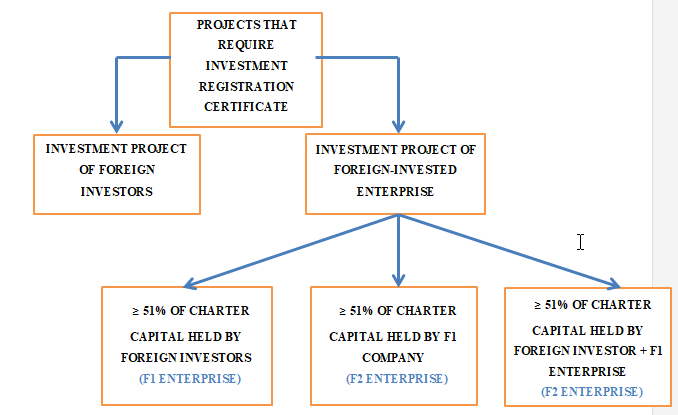
- - Investment projects (establishment of new legal entity in Vietnam, or investment under PPP or BBC) of foreign investors.
- - Investment projects (establishment of new legal entity in Vietnam, or investment under PPP or BBC) of foreign-invested enterprises whose:
- (i) At least 51% of charter capital is held by foreign investors, or the majority of Unlimited Liability Partners is/are foreigner(s) (F1 Enterprise); or
- (ii) At least 51% of charter capital is held by F1 Enterprise (F2 Enterprise); or
- (iii) At least 51% of charter capital is held by foreign investors and F1 Enterprise (F2 Enterprise).
- Pursuant to:
- Clauses 1 and 2 of Article 36; Clauses 1 and 2 of Article 23, Law on Investment 2014.
According to Law on Investment 2014, generally there are 2 processes of registration for IRC:
(1). Process of obtaining Investment In-Principle Approval
(a). Investment In-Principle Approval Issuer:
Depending on the importance of investment project, the authority to issue Investment In-Principle Approval is:
- The National Assembly: Projects that have significant effects on the environment or potentially have seriously affect the environment, including: Nuclear power plants; Project that uses land of national park, relocation of 20,000 people or more in highlands, or 50,000 people or more in other areas.
- The Prime Minister: Important projects such as seaports, airports, petroleum exploitation, refinery, etc. or other projects whose investment capital is 5000 billion VND or more.
- The Provincial People’s Committees: Projects that use land allocated or leased out by the State without auction or bidding; projects that require change of land purposes; Projects that use technologies on the List of technologies restricted to transfer.
(b) Licensing Authority: Provincial Department of Planning and Investment (Provincial DPI – for projects outside industrial parks, export processing zones, hi-tech zones, and economic zones) or Management Board of industrial parks, export-processing zones, hi-tech zones, economic zones.
(c) Statutory timeframe:
- Application for Investment In-Principle Approval:
+ Investment In-Principle Approval by the Provincial People’s Committees: Within 35 days from the date of receipt of project dossier, Licensing Authority shall notify the investor of the result.
+ Investment In-Principle Approval by the Prime Minister: Within 60 days from the date of submission, project dossier shall be appraised by Licensing Authority, relevant local authorities, Provincial People’s Committee and Ministry of Planning and Investment and then submitted for the Prime Minister’s Investment In-Principle Approval.
+ Investment In-Principle Approval by the National Assembly: Usually takes long time because of complex procedure. Ministry of Planning and Investment shall send a report and proposal of establishment of an Appraisal Council to the Prime Minister. The Appraisal Council shall appraise the project dossier and report to the Government, the Government shall then submit for approval of the National Assembly
- Application for IRC: Within 05 working days from the date of receipt of Investment In-Principle Approval, Licensing Authority shall issue IRC.
2. Process of Registration for IRC
For projects that are not required to acquire investment polices approval (mentioned above):
(a) Licensing Authority: Provincial DPI or Management Board of industrial parks, export-processing zones, hi-tech zones, economic zones where the company’s HQ locates.
(b) Statutory timeframe: 15 days from the date of receipt of project dossier.
Pursuant to:
Law on Investment 2014
Decree No.118/2015/ND-CP.
- After obtaining IRC, foreign investors register their business at Business Registration Division under the Provincial DPI where the company’s HQ locates. This process shall be done within 3 working days from the date of receipt of application documents.
- Pursuant to:
- Law on Business 2014
- Decree No.78/2015/ND-CP.
Conditional business lines are the business lines in which the investment must satisfy certain conditions for reasons of national defense and security, social order and security, social ethics, or public health.
The List of Conditional Business Lines is regulated in Annex IV of Law 03/2016/QH14 on “Amendment and Supplement to Article 6 and Annex 4 on the list of Conditional Business Lines Stipulated in the Law on Investment.”
An enterprise is allowed to do conditional business line only if it fulfills all requirements regulated in relevant legal documents. Some major requirements:
- Legal capital (E.g.: 3000 billion VND to open a joint-venture bank, 15 million US$ to open a branch of foreign bank, 5 billion VND to open audit service business, etc.)
- Fire prevention, minimum facility standard, food and hygiene safety (E.g.: restaurant, hotel, education, etc.)
- Certification requirement (E.g.: stock broker certification, consultant certification, etc.)
- Professional liability insurance (E.g.: notary service, lawyer, etc.)
Pursuant to:
Law No. 03/2016/QH14 dated November 22, 2016, on amendment and supplement to Article 6 and Annex 4 on the list of conditional business lines stipulated in the Law on Investment.
a, The foreign investors must follow the procedure to register capital contribution or purchase of shares/capital contribution portion in the following cases:
- The target company runs business in the List of Conditional Business Lines; or
- Capital contribution, capital transfer makes the percent of charter capital owned by foreign investors ≥ 51%.
Procedures:
Step 1: Register to contribute capital, buy shares/capital contribution portion
- Competent Authority: Provincial DPI or Management Board of industrial parks, export-processing zones, hi-tech zones, economic zones where the company’s HQ locates
- Statutory timeframe: 15 days from the date of receipt of project dossier.
Step 2: Amend Business Registration:
After obtaining approval from competent authority, foreign investors and Vietnamese company shall follow the procedure to amend ERC.
- Competent Authority: Provincial DPI or Management Board of industrial parks, export-processing zones, hi-tech zones, economic zones where the company’s HQ locates.
- Statutory timeframe: Within 3 working days from the date of obtaining the competent authority’s approval.
b, Foreign investors other than those mentioned in Paragraph (a) only need to do the procedure to amend the ERC.
Pursuant to:
Article 26 Law on Investment 2014
Clause 3 Article 46 Decree 118/2015/ND-CP
a, Generally, there are 4 major types that apply for most business and investment activities in Vietnam:
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT)
- VAT
- Personal Income Tax (PIT)
- Withholding Tax (consists of corporate income tax and VAT for all foreign entities with or without permanent establishment in Vietnam).
b, Besides, depending on specific business, other taxes may apply such as:
- Special consumption Tax;
- Natural Resources Tax;
- Import Duty;
- Export Duty;
- Environment Protection Tax.
From Jan 1st 2016, the standard Corporate Income Tax rate in Vietnam is 20%.
The CIT rate applicable to petroleum prospecting, exploration and exploitation in Vietnam is between 32% and 50%. The CIT rate applicable to the prospecting, exploration and extraction of precious and rare natural resources (i.e. platinum, gold, silver, tin, tungsten, antimony, gemstones and rare earth other than petroleum) is 50%
Pursuant to:
Article 10 Decree 218/2013/ND-CP
Article 11 Circular 78/2014/TT-BTC
Social Insurance
Health Insurance
Unemployment Insurance
Total
Employee
8%
1.5%
1%
10.5%
Employer
18%
3%
1%
22%
From Jan 1st 2016, monthly insurance payment for employers and employee is calculated based on salary/wage according to labor contract:
Pursuant to:
Decision 959/QĐ-BHXH dated May 09th 2015
According to Law on Housing 2014, beside Vietnamese organization/individual, there are 3 types of foreign entities that are eligible for house ownership and have certain rights relating to house ownership in Vietnam as below:
- Foreign entities who invest in project-based housing construction in Vietnam.
- Foreign-invested enterprises, branches, representative offices of foreign enterprises, foreign-invested funds and branches of foreign banks operating in Vietnam.
- Foreign individuals who are entitled to enter Vietnam but not entitled to diplomatic or consular privileges and immunities.
Pursuant to:
Clause 1 Article 159, Article 160 Law on housing 2014
Payment currency: VND.
Payment account: Foreign currency or VND payment account of foreign individuals.
Fund transfer documents:
- Valid Passport and Visa (ensure that the signing date of the home sales contract is valid within the validity of the Visa), or visa exemption document (if available).
- Home sales contract + Invoice (if available).
- Notice of payment of the investor.
Pursuant to:
Circular 32/2013/TT-NHNN
Documentary 9505/NHNN-QLNH dated December 10th 2015
Decree 99/2015/ND-CP
Web Content Viewer



